

This increase in the relative risk of cerebral palsy is reported to be as high as 20- to 100-fold greater than that in infants with a 5-min Apgar score of 7 to 10 ( 4 4. However, a low 5-min Apgar score clearly confers an increased relative risk of cerebral palsy. Population studies have uniformly reassured us that most neonates with low Apgar scores will not develop cerebral palsy. Williams Obstetrics 24th Edition Study Guide. Cunningham FC, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Dashe JS, Hoffman BL, Casey BM, et al. The 1-min Apgar score reflects the neonatal status at birth and response to resuscitation however, it has not been shown to be associated with long-term clinical outcomes ( 3 3. Committee on Obstetric Practice American Academy of Pediatrics - Committee on Fetus and Newborn.

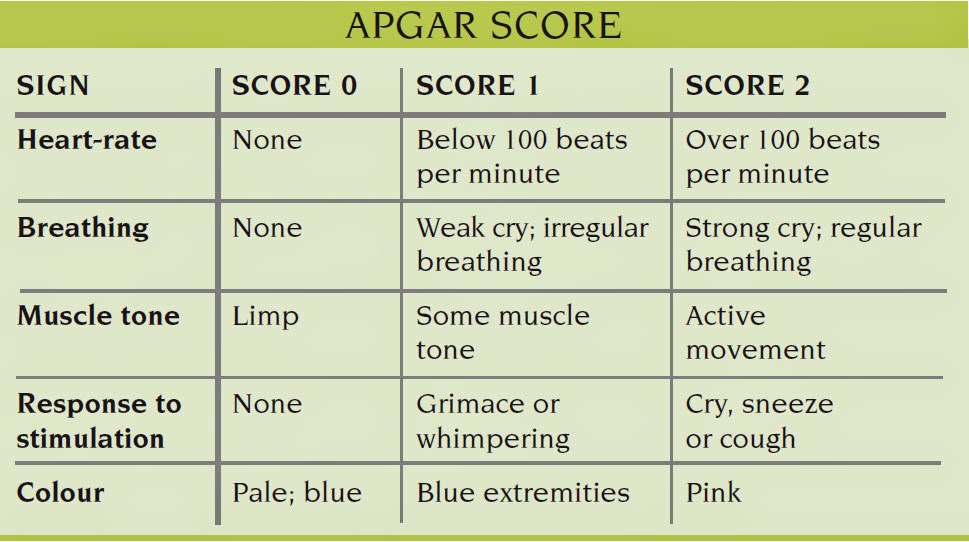
Even after more than half a century since the Apgar score was integrated into routine clinical practice, it remains a standardized, effective, and convenient tool for neonatal assessment ( 2 2. The score is reported at 1 and 5 min after birth for all neonates, and at 5-min intervals thereafter until 20 min for neonates with a score less than 7. Each of these components is assessed and assigned a value of 0, 1, or 2, and the sum of these components is the final score. The Apgar score comprises the following five clinical signs: heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex irritability, and color. A proposal for a new method of evaluation of the newborn infant. Since then, it has been used worldwide for the rapid and standardized assessment of neonates after delivery and for the assessment of the need for prompt intervention to establish breathing at 1 min of age ( 1 1. Virginia Apgar created the Apgar score in 1952. Early detection of risk factors and timely intervention to address these factors may improve neonatal outcomes at birth and reduce the rate of admission to the neonatology department.ġ-min Apgar scores Term neonates Second stage of labor Vaginal delivery Meconium-stained amniotic fluidĭr. Neonates who had low 1-min Apgar scores were more frequently admitted to the neonatology department for further observation or treatment. Multivariate analysis revealed that educational background, body mass index, gestational age, pathological obstetrics, longer duration of the second stage of labor, forceps delivery or vacuum extraction, neonatal weight, neonatal sex, and meconium-stained amniotic fluid were independent risk factors for 1-min Apgar scores <7. Among them, 321 (94.7%) were admitted to the neonatology department for further observation or treatment. Among these 10,550 neonates, 339 (3.2%) had low (score <7) 1-min Apgar scores. Because the 1-min Apgar score reflects neonatal status at birth, we analyzed the risk factors for low (score <7) 1-min Apgar scores through logistic regression. We retrospectively analyzed the maternal and neonatal clinical data of 10,550 infants who were born through vaginal delivery from 37 weeks 0 days to 41 weeks 6 days of single gestation from January 2013 to July 2018. The current study was designed to investigate the perinatal risk factors for low 1-min Apgar scores in term neonates.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
